This is an old revision of the document!
Table of Contents
TGSS-NVSS spectral index maps and catalog
Science team: Francesco de Gasperin (Leiden), Huib T. Intema (Leiden) & Dale A. Frail (NRAO)
We produced a spectral index catalog matching specially re-processed images from two radio surveys at different frequencies: NVSS and TGSS. These surveys were chosen because they are the most sensitive metre and centimetre wavelength surveys currently available, they both cover a large fraction of the sky, and their separation in frequency provides a large lever arm for spectral index calculation. The resulting catalogue includes >1.4 million entries, making it the largest collection of spectral index information to date. Furthermore, we provide the community a spectral index map of 80% of the sky that can be used to classify radio sources.
Catalog
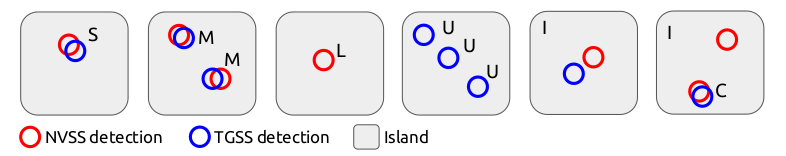
Sources in the catalog are classified into categories:
- single (S): a matched (detection in both NVSS and TGSS) source with no other detections in the same island – these sources are simple, usually point-like or slightly extended in both surveys;
- multiple (M): a matched source with other matched sources (but no unmatched sources) in the same island – these sources are most of the time double-lobe radio galaxies or collections of nearby point sources;
- complex (C): a matched source with unmatched detections in one of the two surveys in the same island – these sources might be part of a more complex object, e.g. a lobe of a radio galaxy where the other lobe is too faint to be detected in one of the surveys;
- upper limit (L): a detection in NVSS with no TGSS detection in the same island – multiple NVSS detections in the island create multiple entries in the catalogue;
- lower limit (U): a detection in TGSS with no NVSS detection in the same island – multiple TGSS detections in the island create multiple entries in the catalogue;
- island (I): if an island is not only made by matched sources (S, M) or unmatched source of the same survey (L, U), the global values of that island are saved as a separate entry – these sources have naturally a poor positional constrain, complex sources (C) are always also part of an island source (I).
The final spectral index catalogue has 1 396 515 entries, of which 503,647 (36%) are full detections (source type: S, C, or M), 845,459 (61%) are lower limits (L), and 6,386 (<1%) are upper limits (U). Entries marked as island (I) are 41,023 (3%). The high number of lower limits is due to the higher sensitivity of NVSS with respect to TGSS.
The spectral index catalog can be downloaded here:
- FITS (111 MB)
Catalog columns:
| Column | Unit | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| RA | degree | S,M,C,I: weighted average of NVSS and TGSS detections |
| DEC | degree | S,M,C,I: weighted average of NVSS and TGSS detections |
| Total_flux_NVSS | Jy | I: sum of detections fluxes; U: set to 0 |
| E_Total_flux_NVSS | Jy | I: quadratic mean of detections' errors; U: set to 0 |
| Peak_flux_NVSS | Jy/beam | I: maximum of detections peak fluxes; U: set to 0 |
| E_Peak_flux_NVSS | Jy/beam | I: error relative to the maximum of detections peak fluxes; U: set to 0 |
| Rms_NVSS | Jy/beam | Local rms noise |
| Total_flux_TGSS | Jy | I: sum of detections fluxes; L: set to 0 |
| E_Total_flux_TGSS | Jy | I: quadratic mean of detections' error; L: set to 0 |
| Peak_flux_TGSS | Jy/beam | I: maximum of detections peak fluxes; L: set to 0 |
| E_Peak_flux_TGSS | Jy/beam | I: error relative to the maximum of detections peak fluxes; L: set to 0 |
| Rms_TGSS | Jy/beam | Local rms noise |
| Spidx | – | Spectral index |
| E_Spidx | – | L,U: set to 0 |
| s2n | – | Peak_flux over Island Rms |
| S_code | S,M,C,L,U,I | Source code as described above |
| Num_match | – | Number of matched sources in the same island |
| Num_unmatch_NVSS | – | Number of NVSS unmatched sources in the same island |
| Num_unmatch_TGSS | – | Number of TGSS unmatched sources in the same island |
| Isl_id | – | Island identification number |
| Source_id | – | Unique source identification number |
Some notes are valid only for specific entry types as saved in the S_code column.
Spectral index map
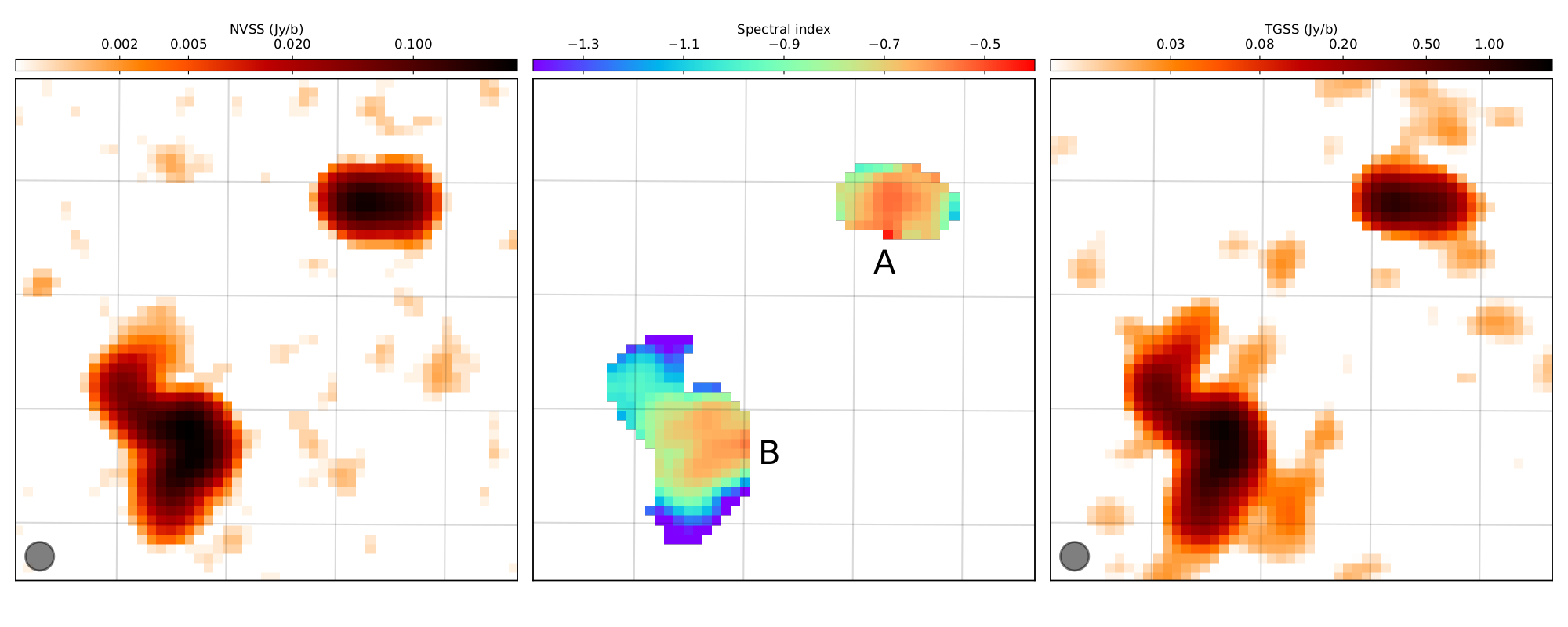
We produced a spectral index map that covers in total 80% of the sky (Dec>-40 deg). The map has been created by extracting a pixel by pixel spectral index value from the NVSS and TGSS images used for the spectral index catalogue. From these images, we retained only those pixels that were at least three times above the noise in both surveys. The output of the process are two maps:
- a spectral index map for all good pixels, each spectral index has been calculated by bootstrapping 1000 times the spectral index value and using the mean of the distribution as estimator;
- a spectral index error map for each good pixel that shows the standard deviation of the bootstrapped distribution.
- Direct access through the web-based Aladin lite tool (limited functionality; pre-loaded images):
- Download and run the Aladin Desktop tool (full functionality)
For option 2, use menu File→Open URL and enter the following links:
- http://tgssadr.strw.leidenuniv.nl/spidx/hips_spidx/ to load the spectral index images
- http://tgssadr.strw.leidenuniv.nl/spidx/hips_spidxerr/ to load the spectral index error images
Two examples of the radio spectral index map produced matching pixel-by-pixel the NVSS and the TGSS maps. Left is the NVSS image, right the TGSS image, at the centre we show the spectral index map:
Acknowledgements
If you use the resources listed in this page, please reference the paper: de Gasperin, Intema & Frail (2017; MNRAS)